Conduit Blueprint Mesh Examples¶
Simulation mesh data is passed to Ascent using a shared set of conventions called the Mesh Blueprint.
Simply described, these conventions outline a structure to follow to create Conduit trees that can represent a wide range of simulation mesh types (uniform grids, unstructured meshes, etc). Conduit’s dynamic tree and zero-copy support make it easy to adapt existing data to conform to the Mesh Blueprint for use in tools like Ascent.
These examples outline how to create Conduit Nodes that describe simple single domain meshes and review some of Conduits built-in mesh examples. More Mesh Blueprint examples are also detailed in Conduit’s Mesh Blueprint Examples Docs .
Creating a uniform grid with a single field¶
#include <iostream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//
// Create a 3D mesh defined on a uniform grid of points
// with a single vertex associated field named `alternating`
//
Node mesh;
int numPerDim = 9;
// create the coordinate set
mesh["coordsets/coords/type"] = "uniform";
mesh["coordsets/coords/dims/i"] = numPerDim;
mesh["coordsets/coords/dims/j"] = numPerDim;
mesh["coordsets/coords/dims/k"] = numPerDim;
// add origin and spacing to the coordset (optional)
mesh["coordsets/coords/origin/x"] = -10.0;
mesh["coordsets/coords/origin/y"] = -10.0;
mesh["coordsets/coords/origin/z"] = -10.0;
double distancePerStep = 20.0/(numPerDim-1);
mesh["coordsets/coords/spacing/dx"] = distancePerStep;
mesh["coordsets/coords/spacing/dy"] = distancePerStep;
mesh["coordsets/coords/spacing/dz"] = distancePerStep;
// add the topology
// this case is simple b/c it's implicitly derived from the coordinate set
mesh["topologies/topo/type"] = "uniform";
// reference the coordinate set by name
mesh["topologies/topo/coordset"] = "coords";
int numVertices = numPerDim*numPerDim*numPerDim; // 3D
float *vals = new float[numVertices];
for (int i = 0 ; i < numVertices ; i++)
vals[i] = ( (i%2)==0 ? 0.0 : 1.0);
// create a vertex associated field named alternating
mesh["fields/alternating/association"] = "vertex";
mesh["fields/alternating/topology"] = "topo";
mesh["fields/alternating/values"].set_external(vals, numVertices);
// print the mesh we created
std::cout << mesh.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// make sure the mesh we created conforms to the blueprint
Node verify_info;
if(!blueprint::mesh::verify(mesh, verify_info))
{
std::cout << "Mesh Verify failed!" << std::endl;
std::cout << verify_info.to_yaml() << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Mesh verify success!" << std::endl;
}
// now lets look at the mesh with Ascent
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// setup actions
Node actions;
Node &add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_scenes";
// declare a scene (s1) with one plot (p1)
// to render the dataset
Node &scenes = add_act["scenes"];
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor";
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "alternating";
// Set the output file name (ascent will add ".png")
scenes["s1/image_prefix"] = "out_ascent_render_uniform";
// print our full actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
// close ascent
a.close();
}
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import numpy as np
#
# Create a 3D mesh defined on a uniform grid of points
# with a single vertex associated field named `alternating`
#
mesh = conduit.Node()
# create the coordinate set
num_per_dim = 9
mesh["coordsets/coords/type"] = "uniform";
mesh["coordsets/coords/dims/i"] = num_per_dim
mesh["coordsets/coords/dims/j"] = num_per_dim
mesh["coordsets/coords/dims/k"] = num_per_dim
# add origin and spacing to the coordset (optional)
mesh["coordsets/coords/origin/x"] = -10.0
mesh["coordsets/coords/origin/y"] = -10.0
mesh["coordsets/coords/origin/z"] = -10.0
distance_per_step = 20.0/(num_per_dim-1)
mesh["coordsets/coords/spacing/dx"] = distance_per_step
mesh["coordsets/coords/spacing/dy"] = distance_per_step
mesh["coordsets/coords/spacing/dz"] = distance_per_step
# add the topology
# this case is simple b/c it's implicitly derived from the coordinate set
mesh["topologies/topo/type"] = "uniform";
# reference the coordinate set by name
mesh["topologies/topo/coordset"] = "coords";
# create a vertex associated field named alternating
num_vertices = num_per_dim * num_per_dim * num_per_dim
vals = np.zeros(num_vertices,dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(num_vertices):
if i%2:
vals[i] = 0.0
else:
vals[i] = 1.0
mesh["fields/alternating/association"] = "vertex";
mesh["fields/alternating/topology"] = "topo";
mesh["fields/alternating/values"].set_external(vals)
# print the mesh we created
print(mesh.to_yaml())
# make sure the mesh we created conforms to the blueprint
verify_info = conduit.Node()
if not conduit.blueprint.mesh.verify(mesh,verify_info):
print("Mesh Verify failed!")
print(verify_info.to_yaml())
else:
print("Mesh verify success!")
# now lets look at the mesh with Ascent
a = ascent.Ascent()
a.open()
# publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh)
# setup actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_scenes";
# declare a scene (s1) with one plot (p1)
# to render the dataset
scenes = add_act["scenes"]
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor"
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "alternating"
# Set the output file name (ascent will add ".png")
scenes["s1/image_name"] = "out_ascent_render_uniform"
# print our full actions tree
print(actions.to_yaml())
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions)
# close ascent
a.close()
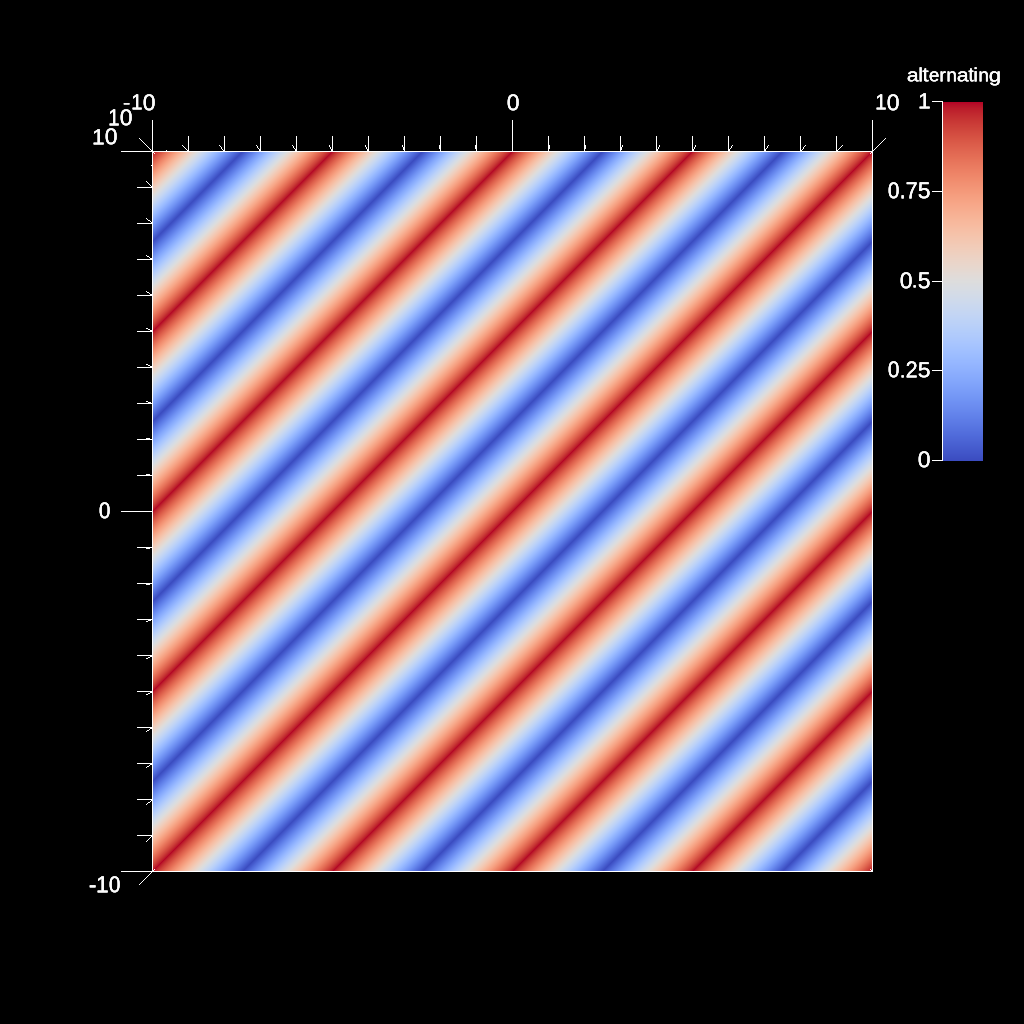
Fig. 2 Example Uniform Mesh Rendered¶
Creating an unstructured tet mesh with fields¶
#include <iostream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//
// Create a 3D mesh defined on an explicit set of points,
// composed of two tets, with two element associated fields
// (`var1` and `var2`)
//
Node mesh;
// create an explicit coordinate set
double X[5] = { -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 };
double Y[5] = { 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 };
double Z[5] = { 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0 };
mesh["coordsets/coords/type"] = "explicit";
mesh["coordsets/coords/values/x"].set_external(X, 5);
mesh["coordsets/coords/values/y"].set_external(Y, 5);
mesh["coordsets/coords/values/z"].set_external(Z, 5);
// add an unstructured topology
mesh["topologies/mesh/type"] = "unstructured";
// reference the coordinate set by name
mesh["topologies/mesh/coordset"] = "coords";
// set topology shape type
mesh["topologies/mesh/elements/shape"] = "tet";
// add a connectivity array for the tets
int64 connectivity[8] = { 0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 3, 1, 2 };
mesh["topologies/mesh/elements/connectivity"].set_external(connectivity, 8);
const int num_elements = 2;
float var1_vals[num_elements] = { 0, 1 };
float var2_vals[num_elements] = { 1, 0 };
// create a field named var1
mesh["fields/var1/association"] = "element";
mesh["fields/var1/topology"] = "mesh";
mesh["fields/var1/values"].set_external(var1_vals, 2);
// create a field named var2
mesh["fields/var2/association"] = "element";
mesh["fields/var2/topology"] = "mesh";
mesh["fields/var2/values"].set_external(var2_vals, 2);
// print the mesh we created
std::cout << mesh.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// make sure the mesh we created conforms to the blueprint
Node verify_info;
if(!blueprint::mesh::verify(mesh, verify_info))
{
std::cout << "Mesh Verify failed!" << std::endl;
std::cout << verify_info.to_yaml() << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Mesh verify success!" << std::endl;
}
// now lets look at the mesh with Ascent
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// setup actions
Node actions;
Node & add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_scenes";
// declare a scene (s1) with one plot (p1)
// to render the dataset
Node &scenes = add_act["scenes"];
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor";
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "var1";
// Set the output file name (ascent will add ".png")
scenes["s1/image_name"] = "out_ascent_render_tets";
// print our full actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
// close ascent
a.close();
}
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import numpy as np
#
# Create a 3D mesh defined on an explicit set of points,
# composed of two tets, with two element associated fields
# (`var1` and `var2`)
#
mesh = conduit.Node()
# create an explicit coordinate set
x = np.array( [-1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ], dtype=np.float64 )
y = np.array( [0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 ], dtype=np.float64 )
z = np.array( [ 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0 ], dtype=np.float64 )
mesh["coordsets/coords/type"] = "explicit";
mesh["coordsets/coords/values/x"].set_external(x)
mesh["coordsets/coords/values/y"].set_external(y)
mesh["coordsets/coords/values/z"].set_external(z)
# add an unstructured topology
mesh["topologies/mesh/type"] = "unstructured"
# reference the coordinate set by name
mesh["topologies/mesh/coordset"] = "coords"
# set topology shape type
mesh["topologies/mesh/elements/shape"] = "tet"
# add a connectivity array for the tets
connectivity = np.array([0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 3, 1, 2 ],dtype=np.int64)
mesh["topologies/mesh/elements/connectivity"].set_external(connectivity)
var1 = np.array([0,1],dtype=np.float32)
var2 = np.array([1,0],dtype=np.float32)
# create a field named var1
mesh["fields/var1/association"] = "element"
mesh["fields/var1/topology"] = "mesh"
mesh["fields/var1/values"].set_external(var1)
# create a field named var2
mesh["fields/var2/association"] = "element"
mesh["fields/var2/topology"] = "mesh"
mesh["fields/var2/values"].set_external(var2)
# print the mesh we created
print(mesh.to_yaml())
# make sure the mesh we created conforms to the blueprint
verify_info = conduit.Node()
if not conduit.blueprint.mesh.verify(mesh,verify_info):
print("Mesh Verify failed!")
print(verify_info.to_yaml())
else:
print("Mesh verify success!")
# now lets look at the mesh with Ascent
a = ascent.Ascent()
a.open()
# publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh)
# setup actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_scenes"
# declare a scene (s1) with one plot (p1)
# to render the dataset
scenes = add_act["scenes"]
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor"
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "var1"
# Set the output file name (ascent will add ".png")
scenes["s1/image_name"] = "out_ascent_render_tets"
# print our full actions tree
print(actions.to_yaml())
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions)
# close ascent
a.close()
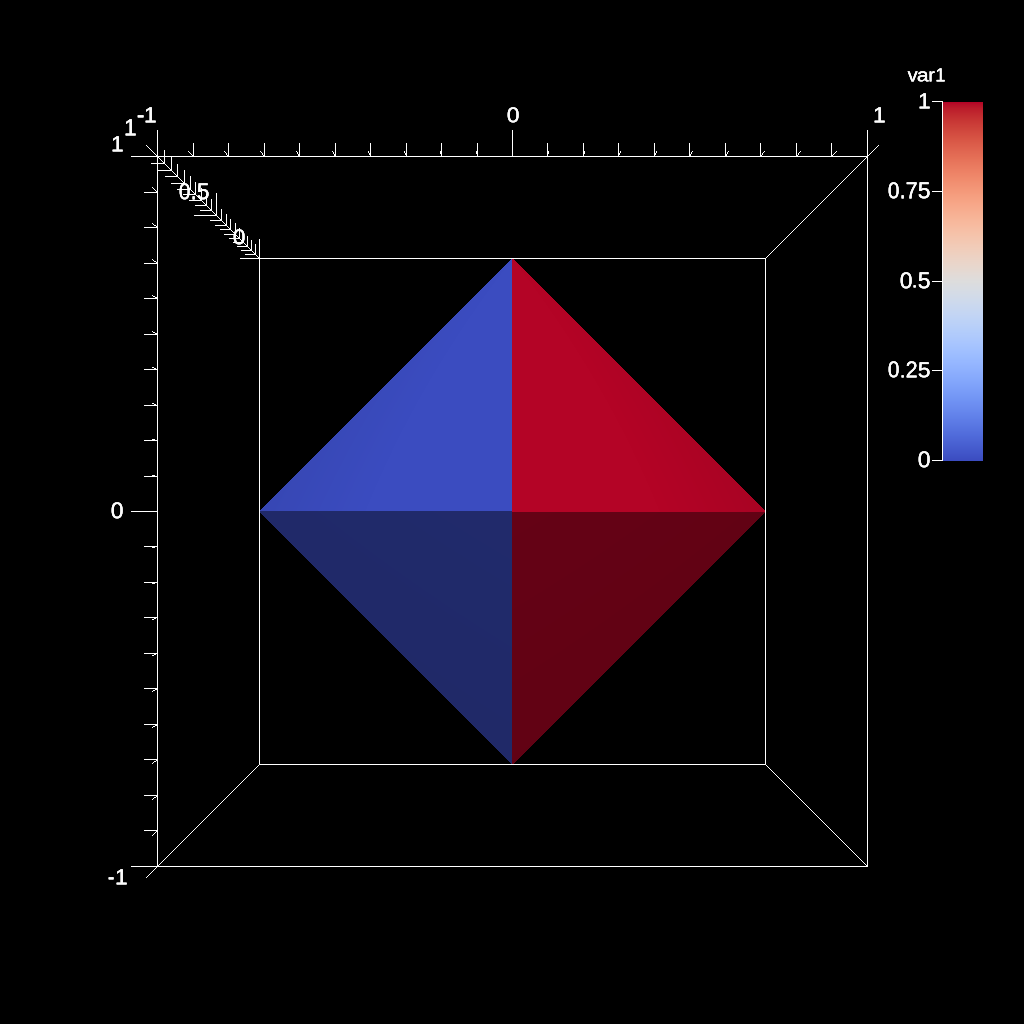
Fig. 3 Example Tet Mesh Rendered¶
Experimenting with the built-in braid example¶
Related docs: Braid .
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <sstream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
const float64 PI_VALUE = 3.14159265359;
// The conduit blueprint library provides several
// simple builtin examples that cover the range of
// supported coordinate sets, topologies, field etc
//
// Here we create a mesh using the braid example
// (https://llnl-conduit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/blueprint_mesh.html#braid)
// and modify one of its fields to create a time-varying
// example
// Define a function that will calcualte a time varying field
void braid_time_varying(int npts_x,
int npts_y,
int npts_z,
float interp,
Node & res)
{
if(npts_z < 1)
npts_z = 1;
int npts = npts_x * npts_y * npts_z;
res["association"] = "vertex";
res["topology"] = "mesh";
float64 *vals_ptr = res["values"].value();
float64 dx_seed_start = 0.0;
float64 dx_seed_end = 5.0;
float64 dx_seed = interp * (dx_seed_end - dx_seed_start) + dx_seed_start;
float64 dy_seed_start = 0.0;
float64 dy_seed_end = 2.0;
float64 dy_seed = interp * (dy_seed_end - dy_seed_start) + dy_seed_start;
float64 dz_seed = 3.0;
float64 dx = (float64) (dx_seed * PI_VALUE) / float64(npts_x - 1);
float64 dy = (float64) (dy_seed * PI_VALUE) / float64(npts_y-1);
float64 dz = (float64) (dz_seed * PI_VALUE) / float64(npts_z-1);
int idx = 0;
for (int k=0; k < npts_z; k++)
{
float64 cz = (k * dz) - (1.5 * PI_VALUE);
for (int j=0; j < npts_y; j++)
{
float64 cy = (j * dy) - PI_VALUE;
for (int i=0; i < npts_x; i++)
{
float64 cx = (i * dx) + (2.0 * PI_VALUE);
float64 cv = sin( cx ) +
sin( cy ) +
2.0 * cos(sqrt( (cx*cx)/2.0 +cy*cy) / .75) +
4.0 * cos( cx*cy / 4.0);
if(npts_z > 1)
{
cv += sin( cz ) +
1.5 * cos(sqrt(cx*cx + cy*cy + cz*cz) / .75);
}
vals_ptr[idx] = cv;
idx++;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// create a conduit node with an example mesh using conduit blueprint's braid function
// ref: https://llnl-conduit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/blueprint_mesh.html#braid
Node mesh;
conduit::blueprint::mesh::examples::braid("hexs",
50,
50,
50,
mesh);
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// create our actions
Node actions;
Node &add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_scenes";
// declare a scene (s1) and plot (p1)
// to render braid field
Node & scenes = add_act["scenes"];
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor";
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "braid";
// print our actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// loop over a set of steps and
// render a time varying version of the braid field
int nsteps = 20;
float64 interp_val = 0.0;
float64 interp_dt = 1.0 / float64(nsteps-1);
for( int i=0; i < nsteps; i++)
{
std::cout << i << ": interp = " << interp_val << std::endl;
// update the braid field
braid_time_varying(50,50,50,interp_val,mesh["fields/braid"]);
// update the mesh cycle
mesh["state/cycle"] = i;
// Set the output file name (ascent will add ".png")
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "out_ascent_render_braid_tv_" << i;
scenes["s1/renders/r1/image_name"] = oss.str();
scenes["s1/renders/r1/camera/azimuth"] = 25.0;
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
interp_val += interp_dt;
}
// close ascent
a.close();
}
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import math
import numpy as np
# The conduit blueprint library provides several
# simple builtin examples that cover the range of
# supported coordinate sets, topologies, field etc
#
# Here we create a mesh using the braid example
# (https://llnl-conduit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/blueprint_mesh.html#braid)
# and modify one of its fields to create a time-varying
# example
# Define a function that will calcualte a time varying field
def braid_time_varying(npts_x, npts_y, npts_z, interp, res):
if npts_z < 1:
npts_z = 1
npts = npts_x * npts_y * npts_z
res["association"] = "vertex"
res["topology"] = "mesh"
vals = res["values"]
dx_seed_start = 0.0
dx_seed_end = 5.0
dx_seed = interp * (dx_seed_end - dx_seed_start) + dx_seed_start
dy_seed_start = 0.0
dy_seed_end = 2.0
dy_seed = interp * (dy_seed_end - dy_seed_start) + dy_seed_start
dz_seed = 3.0
dx = (float) (dx_seed * math.pi) / float(npts_x - 1)
dy = (float) (dy_seed * math.pi) / float(npts_y-1)
dz = (float) (dz_seed * math.pi) / float(npts_z-1)
idx = 0
for k in range(npts_z):
cz = (k * dz) - (1.5 * math.pi)
for j in range(npts_y):
cy = (j * dy) - (math.pi)
for i in range(npts_x):
cx = (i * dx) + (2.0 * math.pi)
cv = math.sin( cx ) + \
math.sin( cy ) + \
2.0 * math.cos(math.sqrt( (cx*cx)/2.0 +cy*cy) / .75) + \
4.0 * math.cos( cx*cy / 4.0)
if npts_z > 1:
cv += math.sin( cz ) + \
1.5 * math.cos(math.sqrt(cx*cx + cy*cy + cz*cz) / .75)
vals[idx] = cv
idx+=1
# create a conduit node with an example mesh using conduit blueprint's braid function
# ref: https://llnl-conduit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/blueprint_mesh.html#braid
mesh = conduit.Node()
conduit.blueprint.mesh.examples.braid("hexs",
50,
50,
50,
mesh)
a = ascent.Ascent()
# open ascent
a.open()
# create our actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act =actions.append()
add_act["action"] = "add_scenes"
# declare a scene (s1) and plot (p1)
# to render braid field
scenes = add_act["scenes"]
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor"
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "braid"
print(actions.to_yaml())
# loop over a set of steps and
# render a time varying version of the braid field
nsteps = 20
interps = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, num=nsteps)
i = 0
for interp in interps:
print("{}: interp = {}".format(i,interp))
# update the braid field
braid_time_varying(50,50,50,interp,mesh["fields/braid"])
# update the mesh cycle
mesh["state/cycle"] = i
# Set the output file name (ascent will add ".png")
scenes["s1/renders/r1/image_name"] = "out_ascent_render_braid_tv_%04d" % i
scenes["s1/renders/r1/camera/azimuth"] = 25.0
# publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh)
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions)
i+=1
# close ascent
a.close()
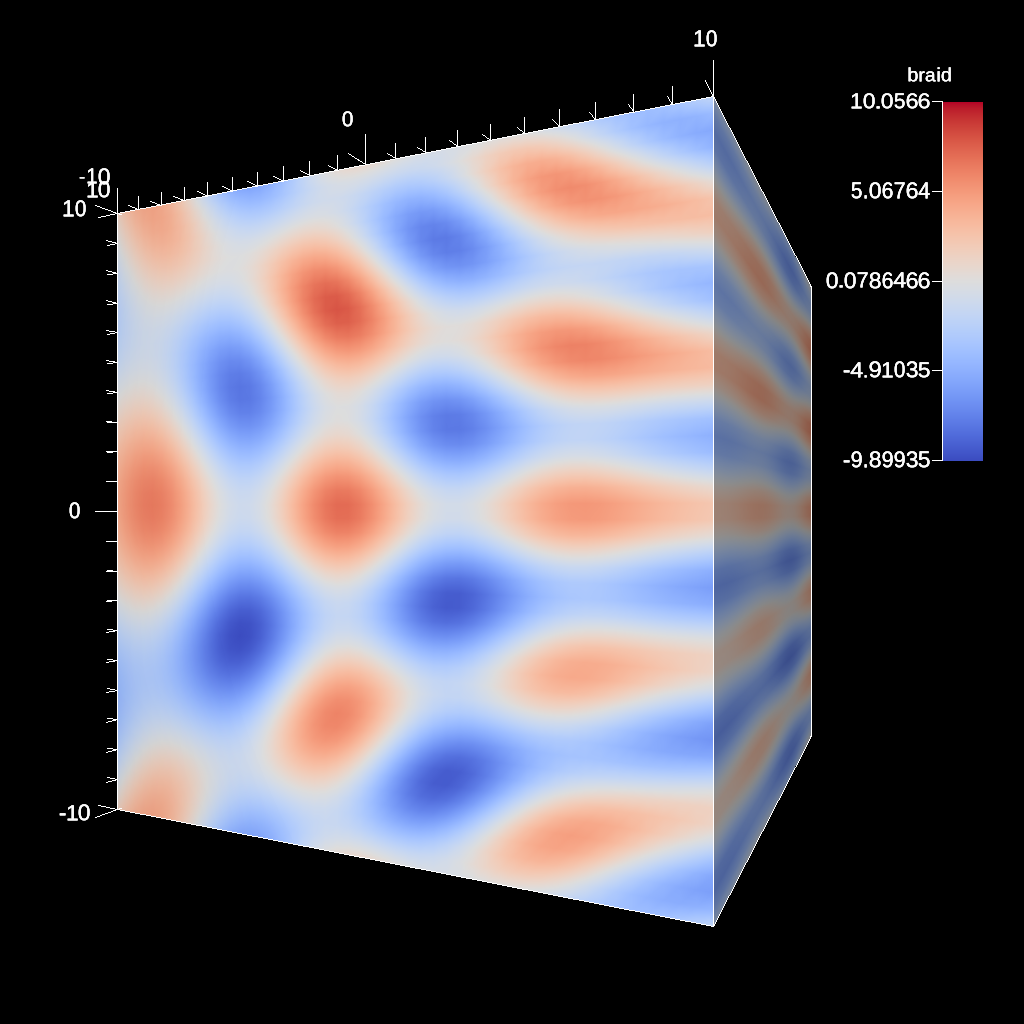
Fig. 4 Final Braid Time-varying Result Rendered¶