Capturing data with Extracts¶
Extracts are the construct that allows users to capture and process data outside Ascent’s pipeline infrastructure. Extract use cases include: Saving mesh data to HDF5 files, creating Cinema databases, and running custom Python analysis scripts. These examples outline how to use several of Ascent’s extracts. See Ascent’s Extracts docs for deeper details on Extracts.
Exporting input mesh data to Blueprint HDF5 files¶
Related docs: Relay
#include <iostream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//create example mesh using the conduit blueprint braid helper
Node mesh;
conduit::blueprint::mesh::examples::braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh);
// Use Ascent to export our mesh to blueprint flavored hdf5 files
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// setup actions
Node actions;
Node &add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_extracts";
// add a relay extract that will write mesh data to
// blueprint hdf5 files
Node &extracts = add_act["extracts"];
extracts["e1/type"] = "relay";
extracts["e1/params/path"] = "out_export_braid_all_fields";
extracts["e1/params/protocol"] = "blueprint/mesh/hdf5";
// print our full actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
// close ascent
a.close();
}
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import numpy as np
mesh = conduit.Node()
conduit.blueprint.mesh.examples.braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh)
# Use Ascent to export our mesh to blueprint flavored hdf5 files
a = ascent.Ascent()
a.open()
# publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh)
# setup actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act = actions.append()
add_act["action"] = "add_extracts"
# add a relay extract that will write mesh data to
# blueprint hdf5 files
extracts = add_act["extracts"]
extracts["e1/type"] = "relay"
extracts["e1/params/path"] = "out_export_braid_all_fields"
extracts["e1/params/protocol"] = "blueprint/mesh/hdf5"
# print our full actions tree
print(actions.to_yaml())
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions)
# close ascent
a.close()
How can you use these files?
You can use them as input to Ascent Replay, which allows you to run Ascent outside of a simulation code.
You can also visualize meshes from these files using VisIt 2.13 or newer.
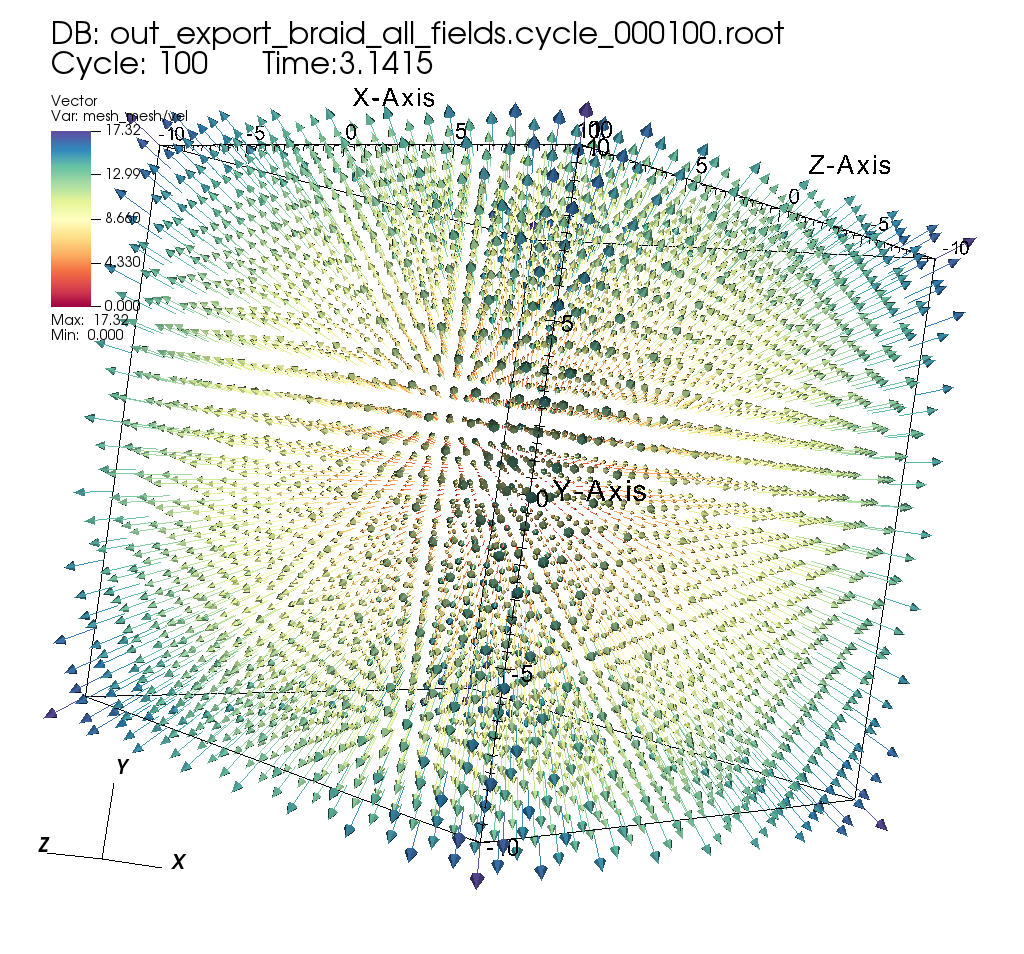
Fig. 15 Exported Mesh Rendered in VisIt¶
VisIt can also export Blueprint HDF5 files, which can be used as input to Ascent Replay.
Blueprint files help bridge in situ and post hoc workflows.
Exporting selected fields from input mesh data to Blueprint HDF5 files¶
Related docs: Relay
#include <iostream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//create example mesh using the conduit blueprint braid helper
Node mesh;
conduit::blueprint::mesh::examples::braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh);
// Use Ascent to export our mesh to blueprint flavored hdf5 files
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// setup actions
Node actions;
Node &add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_extracts";
// add a relay extract that will write mesh data to
// blueprint hdf5 files
Node &extracts = add_act["extracts"];
extracts["e1/type"] = "relay";
extracts["e1/params/path"] = "out_export_braid_one_field";
extracts["e1/params/protocol"] = "blueprint/mesh/hdf5";
//
// add fields parameter to limit the export to the just
// the `braid` field
//
extracts["e1/params/fields"].append().set("braid");
// print our full actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
// close ascent
a.close();
}
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import numpy as np
mesh = conduit.Node()
conduit.blueprint.mesh.examples.braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh)
# Use Ascent to export our mesh to blueprint flavored hdf5 files
a = ascent.Ascent()
a.open()
# publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
# setup actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act = actions.append()
add_act["action"] = "add_extracts"
# add a relay extract that will write mesh data to
# blueprint hdf5 files
extracts = add_act["extracts"]
extracts["e1/type"] = "relay"
extracts["e1/params/path"] = "out_export_braid_one_field"
extracts["e1/params/protocol"] = "blueprint/mesh/hdf5"
#
# add fields parameter to limit the export to the just
# the `braid` field
#
extracts["e1/params/fields"].append().set("braid")
# print our full actions tree
print(actions.to_yaml())
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
a.close()
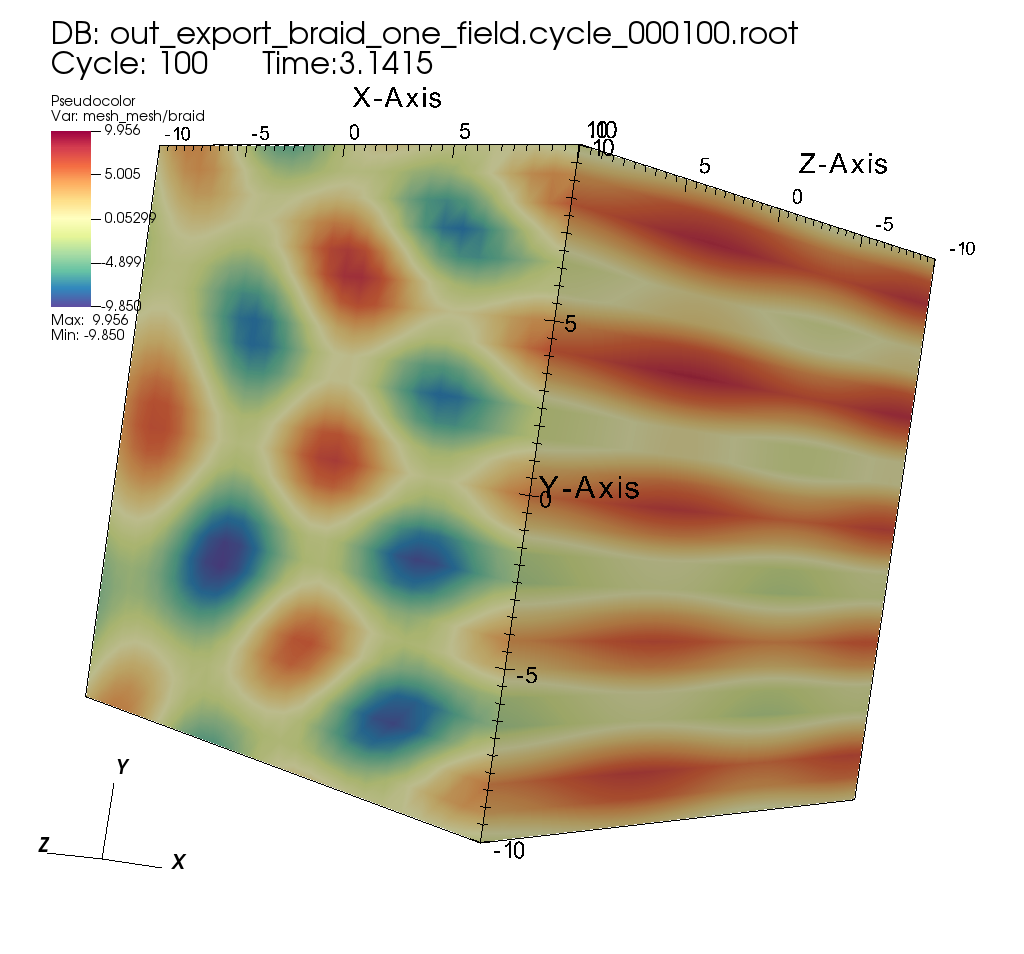
Fig. 16 Exported Mesh Rendered in VisIt¶
Exporting the result of a pipeline to Blueprint HDF5 files¶
Related docs: Relay
#include <iostream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//create example mesh using the conduit blueprint braid helper
Node mesh;
conduit::blueprint::mesh::examples::braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh);
// Use Ascent to export contours to blueprint flavored hdf5 files
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// setup actions
Node actions;
Node &add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_pipelines";
Node &pipelines = add_act["pipelines"];
// create a pipeline (pl1) with a contour filter (f1)
pipelines["pl1/f1/type"] = "contour";
// extract contours where braid variable
// equals 0.2 and 0.4
Node &contour_params = pipelines["pl1/f1/params"];
contour_params["field"] = "braid";
double iso_vals[2] = {0.2, 0.4};
contour_params["iso_values"].set(iso_vals,2);
// add an extract to capture the pipeline result
Node &add_act2 = actions.append();
add_act2["action"] = "add_extracts";
Node &extracts = add_act2["extracts"];
// add an relay extract (e1) to export the pipeline result
// (pl1) to blueprint hdf5 files
extracts["e1/type"] = "relay";
extracts["e1/pipeline"] = "pl1";
extracts["e1/params/path"] = "out_extract_braid_contour";
extracts["e1/params/protocol"] = "blueprint/mesh/hdf5";
// print our full actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
// close ascent
a.close();
}
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import numpy as np
mesh = conduit.Node()
conduit.blueprint.mesh.examples.braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh)
# Use Ascent to calculate and render contours
a = ascent.Ascent()
a.open()
# publish our mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
# setup actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_pipelines"
pipelines = add_act["pipelines"]
# create a pipeline (pl1) with a contour filter (f1)
pipelines["pl1/f1/type"] = "contour"
# extract contours where braid variable
# equals 0.2 and 0.4
contour_params = pipelines["pl1/f1/params"]
contour_params["field"] = "braid"
iso_vals = np.array([0.2, 0.4],dtype=np.float32)
contour_params["iso_values"].set(iso_vals)
# add an extract to capture the pipeline result
add_act2 = actions.append()
add_act2["action"] = "add_extracts"
extracts = add_act2["extracts"]
# add an relay extract (e1) to export the pipeline result
# (pl1) to blueprint hdf5 files
extracts["e1/type"] = "relay"
extracts["e1/pipeline"] = "pl1"
extracts["e1/params/path"] = "out_extract_braid_contour"
extracts["e1/params/protocol"] = "blueprint/mesh/hdf5"
# print our full actions tree
print(actions.to_yaml())
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
a.close()
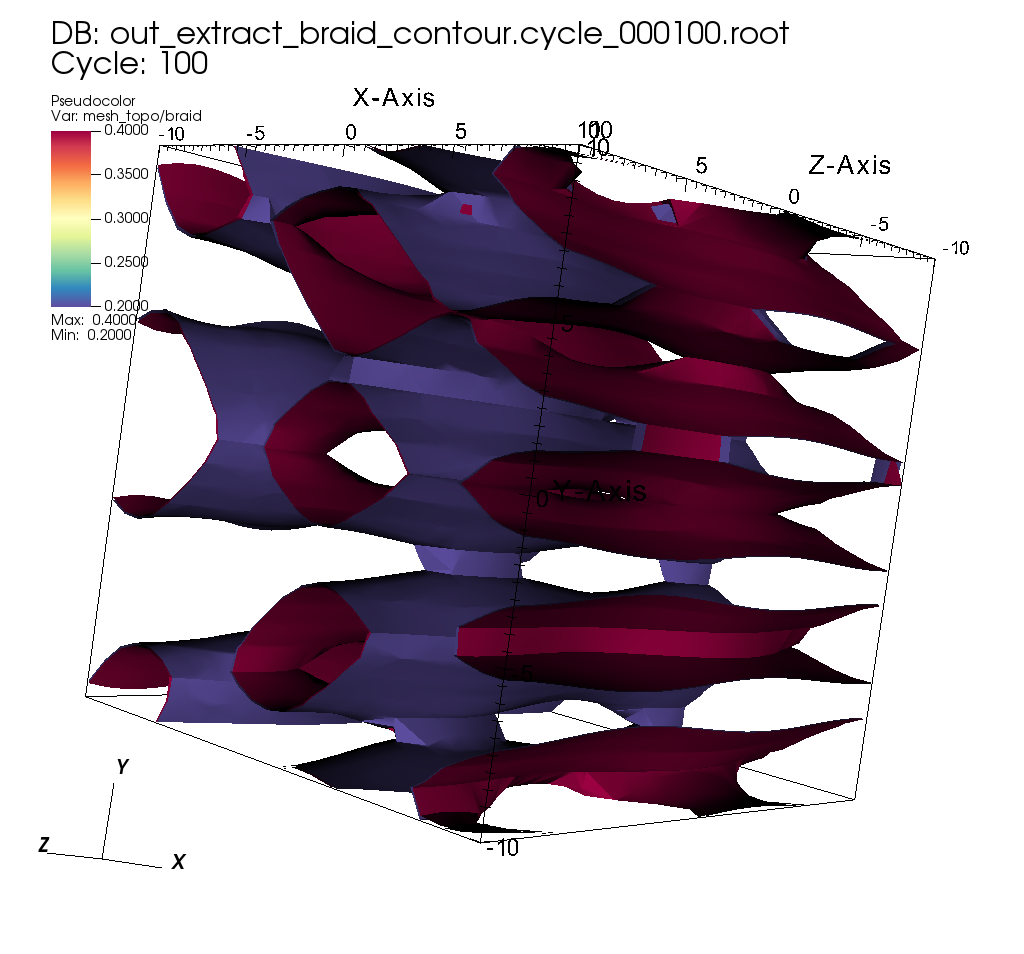
Fig. 17 Exported Mesh Rendered in VisIt¶
Creating a Cinema image database for post-hoc exploration¶
Related docs: Cinema Databases
#include <iostream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//create example mesh using the conduit blueprint braid helper
Node mesh;
conduit::blueprint::mesh::examples::braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh);
// Use Ascent to create a Cinema Image Database
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// setup actions
Node actions;
Node &add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_pipelines";
Node &pipelines = add_act["pipelines"];
// create a pipeline (pl1) with a contour filter (f1)
pipelines["pl1/f1/type"] = "contour";
// extract contours where braid variable
// equals 0.2 and 0.4
Node &contour_params = pipelines["pl1/f1/params"];
contour_params["field"] = "braid";
double iso_vals[2] = {0.2, 0.4};
contour_params["iso_values"].set(iso_vals,2);
// declare a scene to render several angles of
// the pipeline result (pl1) to a Cinema Image
// database
Node &add_act2 = actions.append();
add_act2["action"] = "add_scenes";
Node &scenes = add_act2["scenes"];
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor";
scenes["s1/plots/p1/pipeline"] = "pl1";
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "braid";
// select cinema path
scenes["s1/renders/r1/type"] = "cinema";
// use 5 renders in phi
scenes["s1/renders/r1/phi"] = 5;
// and 5 renders in theta
scenes["s1/renders/r1/theta"] = 5;
// setup to output database to:
// cinema_databases/out_extract_cinema_contour
// you can view using a webserver to open:
// cinema_databases/out_extract_cinema_contour/index.html
scenes["s1/renders/r1/db_name"] = "out_extract_cinema_contour";
// print our full actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
// close ascent
a.close();
}
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import numpy as np
mesh = conduit.Node()
conduit.blueprint.mesh.examples.braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh)
a = ascent.Ascent()
a.open()
# publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
# setup actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_pipelines"
pipelines = add_act["pipelines"]
# create a pipeline (pl1) with a contour filter (f1)
pipelines["pl1/f1/type"] = "contour"
# extract contours where braid variable
# equals 0.2 and 0.4
contour_params = pipelines["pl1/f1/params"]
contour_params["field"] = "braid"
iso_vals = np.array([0.2, 0.4],dtype=np.float32)
contour_params["iso_values"].set(iso_vals)
# declare a scene to render several angles of
# the pipeline result (pl1) to a Cinema Image
# database
add_act2 = actions.append()
add_act2["action"] = "add_scenes"
scenes = add_act2["scenes"]
scenes["s1/plots/p1/type"] = "pseudocolor"
scenes["s1/plots/p1/pipeline"] = "pl1"
scenes["s1/plots/p1/field"] = "braid"
# select cinema path
scenes["s1/renders/r1/type"] = "cinema"
# use 5 renders in phi
scenes["s1/renders/r1/phi"] = 5
# and 5 renders in theta
scenes["s1/renders/r1/theta"] = 5
# setup to output database to:
# cinema_databases/out_extract_cinema_contour
# you can view using a webserver to open:
# cinema_databases/out_extract_cinema_contour/index.html
scenes["s1/renders/r1/db_name"] = "out_extract_cinema_contour"
# print our full actions tree
print(actions.to_yaml())
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
a.close()
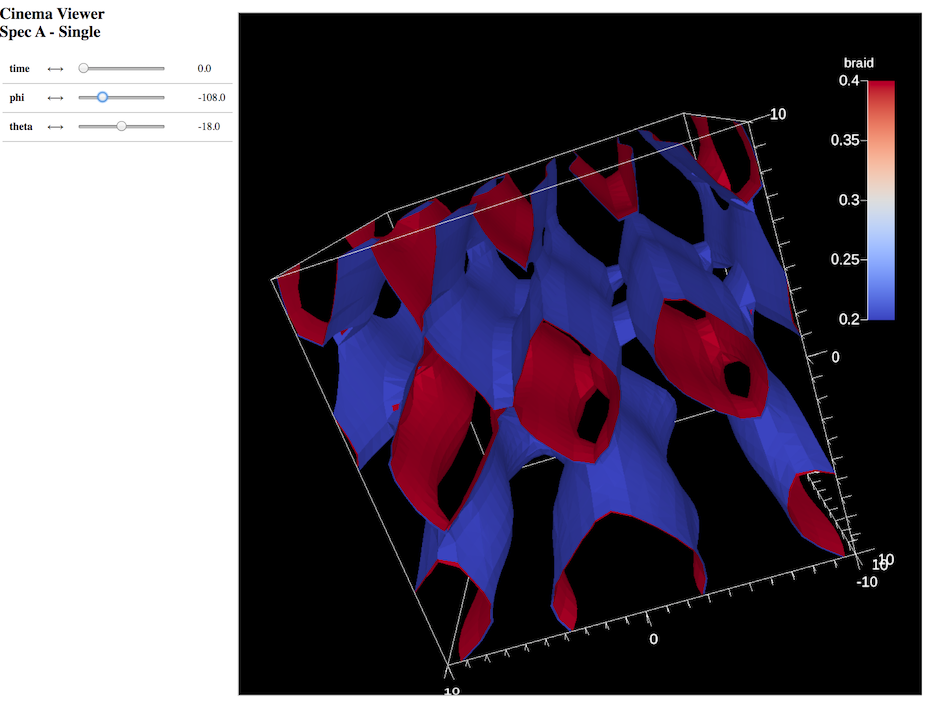
Fig. 18 Snapshot of Cinema Database Result¶
Using a Python Extract to execute custom Python analysis¶
Related docs: Python
#include <iostream>
#include "ascent.hpp"
#include "conduit_blueprint.hpp"
using namespace ascent;
using namespace conduit;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//create example mesh using the conduit blueprint braid helper
Node mesh;
conduit::blueprint::mesh::examples::braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh);
// Use Ascent to execute a python script
// that computes a histogram
Ascent a;
// open ascent
a.open();
// publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
// setup actions
Node actions;
Node &add_act = actions.append();
add_act["action"] = "add_extracts";
// add an extract to execute custom python code
// in `ascent_tutorial_python_extract_braid_histogram.py`
//
// This extract script runs the same histogram code as above,
// but saves the output to `out_py_extract_hist_results.yaml`
//
Node &extracts = add_act["extracts"];
extracts["e1/type"] = "python";
extracts["e1/params/file"] = "ascent_tutorial_python_extract_braid_histogram.py";
// print our full actions tree
std::cout << actions.to_yaml() << std::endl;
// execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
// close ascent
a.close();
}
Output
Energy extents: -9.850344080110776 9.956328748632988
Histogram of Energy:
Counts:
[ 13 23 33 55 85 102 135 153 220 211 254 267 312 339 365 377 428 486
555 537 594 635 681 683 685 688 635 606 629 530 475 480 474 466 360 366
349 284 243 202 167 120 104 72 60 45 21 11 10]
Bin Edges:
[-9.85034408 -9.44612627 -9.04190845 -8.63769064 -8.23347283 -7.82925502
-7.4250372 -7.02081939 -6.61660158 -6.21238376 -5.80816595 -5.40394814
-4.99973033 -4.59551251 -4.1912947 -3.78707689 -3.38285907 -2.97864126
-2.57442345 -2.17020564 -1.76598782 -1.36177001 -0.9575522 -0.55333438
-0.14911657 0.25510124 0.65931905 1.06353687 1.46775468 1.87197249
2.2761903 2.68040812 3.08462593 3.48884374 3.89306156 4.29727937
4.70149718 5.10571499 5.50993281 5.91415062 6.31836843 6.72258625
7.12680406 7.53102187 7.93523968 8.3394575 8.74367531 9.14789312
9.55211094 9.95632875]
import conduit
import conduit.blueprint
import ascent
import numpy as np
mesh = conduit.Node()
conduit.blueprint.mesh.examples.braid("hexs",
25,
25,
25,
mesh)
#
# Ascent provides an embedded Python environment to support
# custom analysis. When using MPI this environment supports
# distributed-memory processing with one Python interpreter
# per MPI task.
#
# You can use this environment in Ascent's Python Extract.
#
# In the case you are already using Ascent from Python this may
# appear a bit odd. Yes, this feature is most useful to
# provide a Python analysis environment to simulation codes written
# in other lanauges (C++, C, or Fortran). Reguardless, we can
# still access it and leverage it from Python.
#
#
# For more detials about the Python extract, see:
# https://ascent.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Actions/Extracts.html#python
#
#
# First, we a histogram calcuation directly in our current
# Python interpreter and then we will compare results
# with running the same code via a Python Extract.
#
# fetch the numpy array for the braid field values
e_vals = mesh["fields/braid/values"]
# find the data extents of the braid field
e_min, e_max = e_vals.min(), e_vals.max()
# compute bins on extents
bins = np.linspace(e_min, e_max)
# get histogram counts
hist, bin_edges = np.histogram(e_vals, bins = bins)
print("\nEnergy extents: {} {}\n".format(e_min, e_max))
print("Histogram of Energy:\n")
print("Counts:")
print(hist)
print("\nBin Edges:")
print(bin_edges)
print("")
# save our results to a yaml file
hist_results = conduit.Node()
hist_results["hist"] = hist
hist_results["bin_edges"] = bin_edges
hist_results.save("out_hist_results.yaml","yaml")
# Use Ascent to execute the histogram script.
a = ascent.Ascent()
ascent_opts = conduit.Node()
ascent_opts["exceptions"] = "forward"
a.open(ascent_opts)
# publish mesh to ascent
a.publish(mesh);
# setup actions
actions = conduit.Node()
add_act = actions.append()
add_act["action"] = "add_extracts"
# add an extract to execute custom python code
# in `ascent_tutorial_python_extract_braid_histogram.py`
#
# This extract script runs the same histogram code as above,
# but saves the output to `out_py_extract_hist_results.yaml`
#
extracts = add_act["extracts"]
extracts["e1/type"] = "python"
extracts["e1/params/file"] = "ascent_tutorial_python_extract_braid_histogram.py"
# print our full actions tree
print(actions.to_yaml())
# execute the actions
a.execute(actions);
# close ascent
a.close()
#
# Load and compare the extract yaml results,
# they should match our earlier results.
#
hist_extract_results = conduit.Node()
hist_extract_results.load("out_py_extract_hist_results.yaml",protocol="yaml")
diff_info = conduit.Node()
# hist_results is a Node with our earlier results
if hist_results.diff(hist_extract_results,diff_info):
print("Extract results differ!")
print(diff_info.to_yaml())
else:
print("Extract results match.")
Output
Energy extents: -9.850344080110776 9.956328748632988
Histogram of Energy:
Counts:
[ 13 23 33 55 85 102 135 153 220 211 254 267 312 339 365 377 428 486
555 537 594 635 681 683 685 688 635 606 629 530 475 480 474 466 360 366
349 284 243 202 167 120 104 72 60 45 21 11 10]
Bin Edges:
[-9.85034408 -9.44612627 -9.04190845 -8.63769064 -8.23347283 -7.82925502
-7.4250372 -7.02081939 -6.61660158 -6.21238376 -5.80816595 -5.40394814
-4.99973033 -4.59551251 -4.1912947 -3.78707689 -3.38285907 -2.97864126
-2.57442345 -2.17020564 -1.76598782 -1.36177001 -0.9575522 -0.55333438
-0.14911657 0.25510124 0.65931905 1.06353687 1.46775468 1.87197249
2.2761903 2.68040812 3.08462593 3.48884374 3.89306156 4.29727937
4.70149718 5.10571499 5.50993281 5.91415062 6.31836843 6.72258625
7.12680406 7.53102187 7.93523968 8.3394575 8.74367531 9.14789312
9.55211094 9.95632875]
-
action: "add_extracts"
extracts:
e1:
type: "python"
params:
file: "ascent_tutorial_python_extract_braid_histogram.py"
Energy extents: -9.850344080110776 9.956328748632988
Histogram of Energy:
Counts:
[ 13 23 33 55 85 102 135 153 220 211 254 267 312 339 365 377 428 486
555 537 594 635 681 683 685 688 635 606 629 530 475 480 474 466 360 366
349 284 243 202 167 120 104 72 60 45 21 11 10]
Bin Edges:
[-9.85034408 -9.44612627 -9.04190845 -8.63769064 -8.23347283 -7.82925502
-7.4250372 -7.02081939 -6.61660158 -6.21238376 -5.80816595 -5.40394814
-4.99973033 -4.59551251 -4.1912947 -3.78707689 -3.38285907 -2.97864126
-2.57442345 -2.17020564 -1.76598782 -1.36177001 -0.9575522 -0.55333438
-0.14911657 0.25510124 0.65931905 1.06353687 1.46775468 1.87197249
2.2761903 2.68040812 3.08462593 3.48884374 3.89306156 4.29727937
4.70149718 5.10571499 5.50993281 5.91415062 6.31836843 6.72258625
7.12680406 7.53102187 7.93523968 8.3394575 8.74367531 9.14789312
9.55211094 9.95632875]
Extract results match.